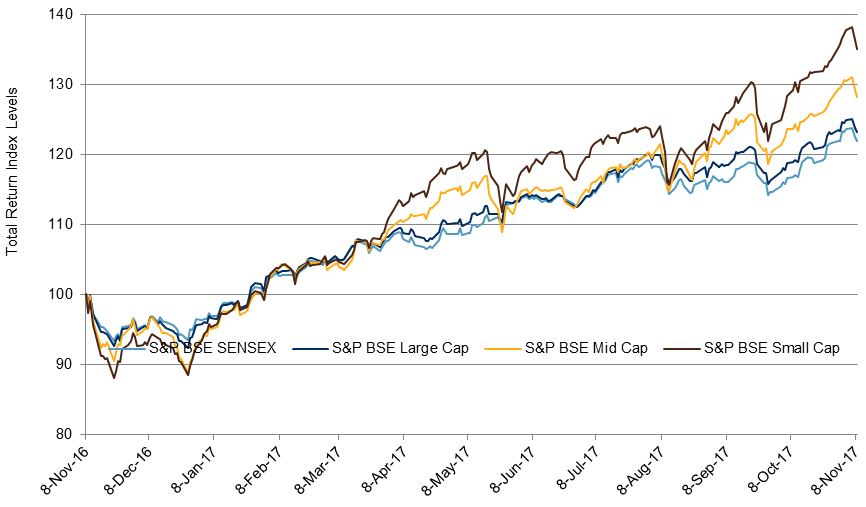
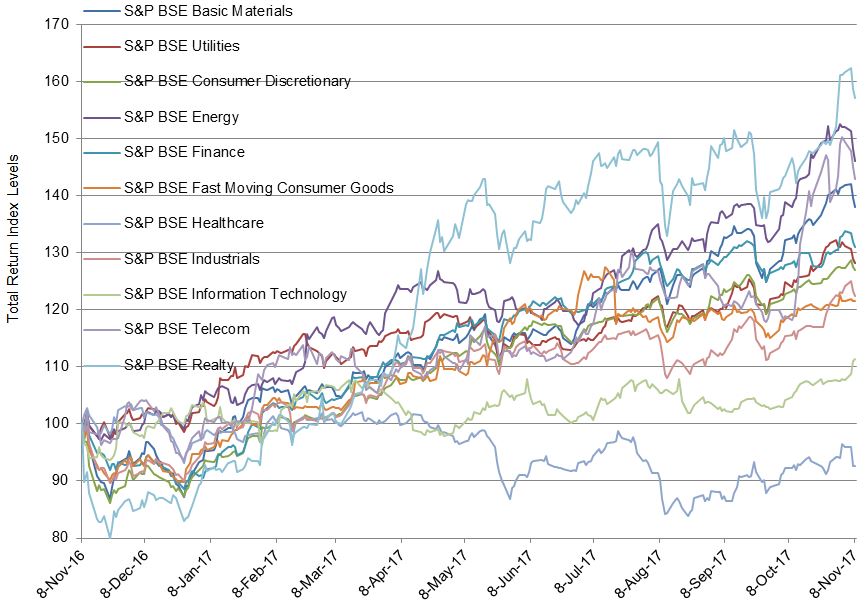
There’s still some time remaining in 2017, but if it goes the way the year has thus far, this will be the least volatile year for the S&P 500 in 22 years. Given this context, selection to the S&P 500® Low Volatility Index (an index of the 100 least volatile stocks in the S&P 500) recently has mostly been about which stocks have declined in volatility the most. In each of the last four rebalances, average realized volatility for the stocks in Low Vol has declined compared to the previous rebalance.
In the latest rebalance, Utilities regained its usual prominence, adding 5%; at 22% of Low Vol, it is currently the biggest sector in the index. This came mostly at the expense of Consumer Staples, whose weight declined to 9% from 13%. Real Estate’s weight doubled to 6%. Curiously, although underweighted compared to the S&P 500, Technology maintains a significant weight in Low Vol (the sector’s standing ballooned in the rebalance in May 2017.)
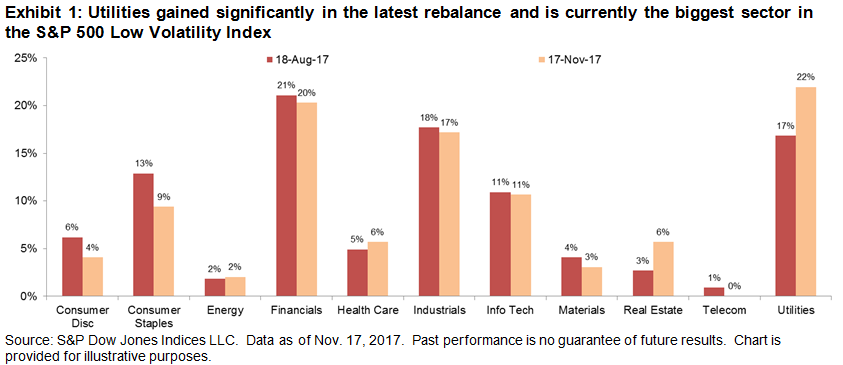
As a rule of thumb, sector level volatility usually provides good insight into the S&P 500 Low Volatility Index, even though the index’s methodology is entirely focused at the stock level. For the latest rebalance, however, sectoral volatility was only part of the picture. For the year ended October 31, 2017, all sectors declined in volatility with the exception of Technology and Telecom. Unsurprisingly, Telecom has left Low Vol altogether.
Volatility at the sector level declined the most for Energy, but there was little change in Energy’s weight in Low Vol from the previous rebalance. Meanwhile, volatility at the sector level rose for Technology, yet there was also little change in its weight in Low Vol. This would suggest that there was a wide range of volatility within both sectors, and that stock selection was more meaningful than the sectoral effect.