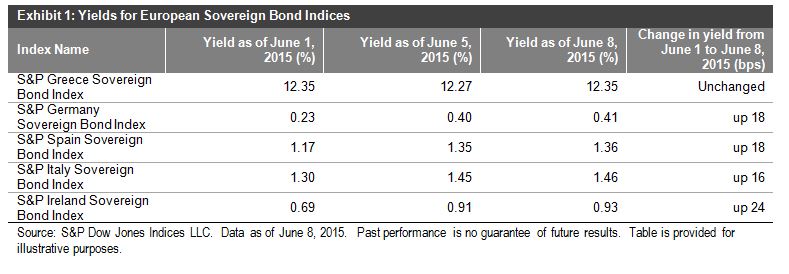
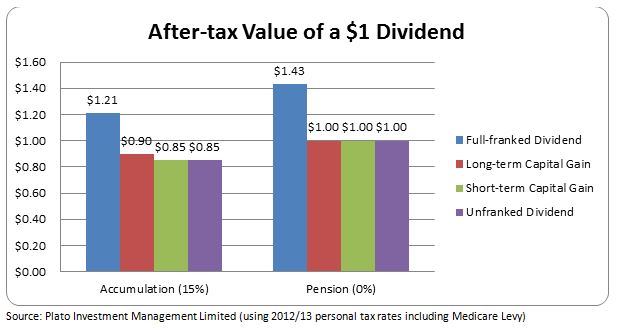
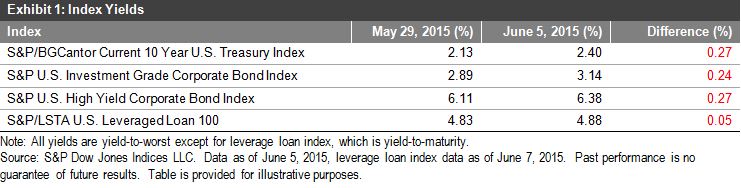
Investors have spoken: There is a world outside of traditional indexing, and they want in.
“Smart beta” or factor indices bridge the gap between active and passive management by allowing investors to tilt toward specific investment attributes – for example, low volatility or high dividend yield. These indices use factors in a rules-based, transparent manner to determine index composition and/or weighting. Smart beta products give passive investors access to factor exposures that were once only available through active management.
Smart beta has flourished, attracting more assets than ever before. According to our 2014 Survey of Indexed Assets, AUM in products linked to S&P DJI smart beta indices grew 55% in 2014. As the demand for factor indices has increased, so too has their availability. We’ve created indices to provide a wide variety of exposures, while still maintaining the advantages of passive management. The growth of ETFs as a delivery vehicle has complemented the growth of factor indices, enabling investors to seek new opportunities.
That said, demand for smart beta has not been cannibalistic; passive investment in traditional exposures has also increased. AUM growth in products indexed to the S&P 500 outpaced the growth of the index, indicating positive net flows into traditional cap-weighted investments. The demand for first-generation indexed investments has not decreased in the wake of new “smart” offerings.
Much research (including our SPIVA reports) confirms that most active managers underperform most of the time. The probability that an active manager beat his benchmark is low, and the probability that he did it consistently is even lower. Positive inflows into passive vehicles indicate that investors have heeded these data, and that the smarter investor prefers better odds.
The posts on this blog are opinions, not advice. Please read our Disclaimers.