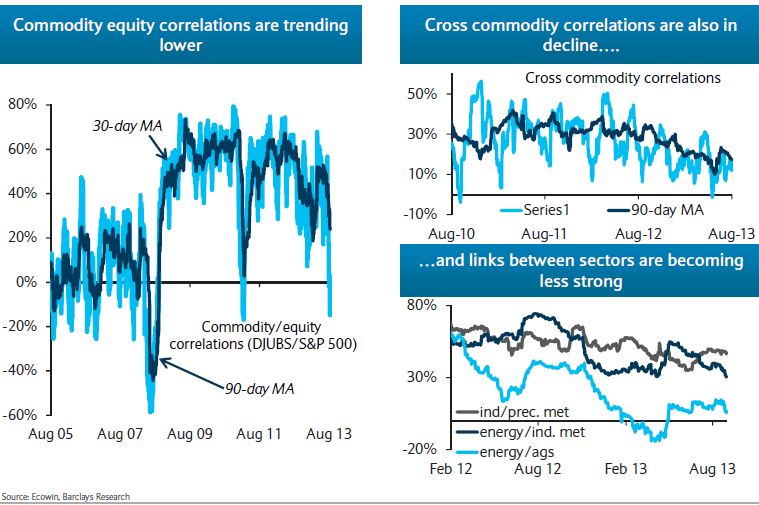
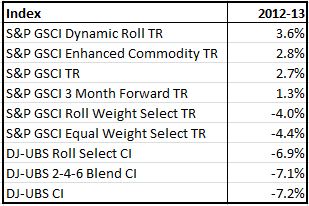
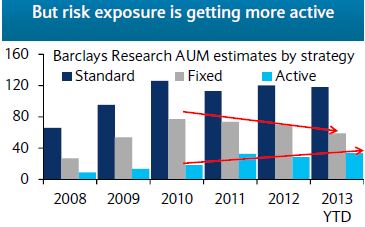
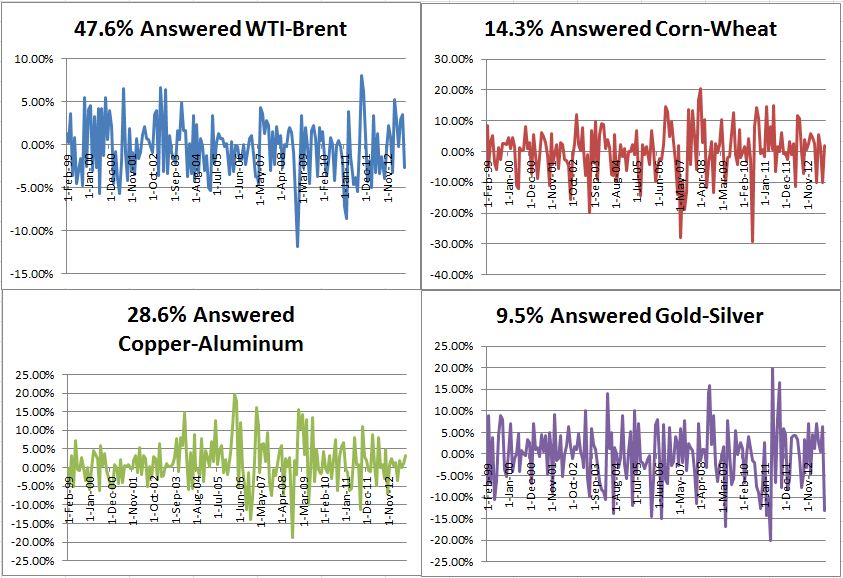
As of the market close on Monday, Congress is still pushing bills back and forth from one house to the other and a government shutdown looks like the odds-on bet. The S&P 500 rebounded part way from a sharp drop at the open but has done little since mid-morning. If the Credit Default Swap market is any indication, the shutdown could be followed by a debt ceiling impasse. The markets are saying the shutdowns matter and the debt ceiling matters even more.
Shutting the government down for a few days will cost. In 1996 the bill was about $100 million per day due to delays, disruptions and time spent recovering from the shutdown. The larger damage is probably to how we feel our government and how it looks to others. Analysts and commentators criticize some European nations which can’t seem to pass a budget, collect taxes or keep a government in office for more than a few months. If the US begins to look and act that way, can we expect investors – either foreign or domestic – to have confidence in our markets? The cost of a government shutdown is not $100 million a day or delaying next Friday’s employment report, it is the loss of confidence.
The debt ceiling is another matter. The damage would be severe as explained in comments today from the New York Times and the Financial Times. If the debt ceiling isn’t raised the President will face a three-way choice: slash an estimated $600 billion from spending immediately, default on maturing US treasury bills, notes and bonds or ignore the debt ceiling. Slashing that much spending would mean the government really shuts down – no social security payments, no salaries, no contracts with payment due, nothing at all. Defaulting on the debt would be worse. In 2008 when Lehman Brothers went bankrupt, the financial system froze because no one would trust the collateral behind Repos. (Repos, repurchase agreements, are the ways banks, brokers, corporations and money market funds invest overnight.) Without Repos, there is no access to large amounts of short term overnight credit. If there is a default, repos with treasury collateral won’t be accepted. If all the other options are terrible, the one that’s left is to ignore the debt ceiling. No matter which choice the President makes, the markets are likely to react badly.
The posts on this blog are opinions, not advice. Please read our Disclaimers.